| Русский / English |
|

|
NUCLEAR SAFETY INSTITUTE OF THE
RUSSIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
|
EMERGENCY RESPONSE AND RADIATION MONITORING
- Models and Computer Systems
- Technical Crisis Center of Nuclear Safety Institute (IBRAE RAN)
- Regional Emergency-response and Radiation-monitoring Systems
- Practical Experience
- Trainings and Exercises
- Meteorological threads in the regions of NRHO (nuclear and radiation hazardous object) location
The history of IBRAE RAN began with the activities of the expert group of physicists, which took an active part in mitigation of the consequences of the Chernobyl accident under the leadership of L.A. Bolshov. The group demonstrated the high efficiency in assessing and forecasting the accident evolution at the 4th ChNPP Unit and in development of practical measures to contain the accident and to organize radiation monitoring near ChNPP. Subsequently this group of experts became the nucleus of new institute. Organizational structure and main activities of the Institute, to a large extent, resulted from comprehension of the Chernobyl experience.
Therefore, the issues of emergency response have always been paid special attention at IBRAE RAN. Since 1996, the Nuclear Safety Institute is an active participant of activities within the national system of emergency response in the crisis situations at nuclear and radiation hazardous facilities. It provides scientific and technical support to CC of Rosenergoatom Concern, SCC of Rosatom and National Emergency Management Center of EMERCOM in protection of population and areas during possible radiation incidents.
THE MAIN ACTIVITIES OF IBRAE RAN IN THE FIELD OF EMERGENCY RESPONSE AND RADIATION MONITORING
More than sixty years of experience of domestic and global nuclear energy give reason to assert that one of the key factors in ensuring safety of nuclear and radiation hazardous facilities (NRHF) is the creation and optimization of radiation monitoring and emergency response system. Such a system requires a specialized emergency response structures, interaction and quick information exchange between these structures and public authorities at all levels, scientific and technical support of decision making.
In accordance with the "Concept of Long-Term Socio-Economic Development of the Russian Federation for the period till 2020", radiation safety for population and environment is one of the priority directions of development of the country. This calls for continuous improvement of radiation monitoring and emergency response systems.
The main factors determining their effectiveness include:
- Coordination of authorized institutions engaged in emergency response functions, and authorities at the municipal, regional and national levels;
- Availability of specialized centers, which promptly provide qualified scientific, technical and expert support to authorized entities and authorities in making the decisions on population and environment protection;
- Availability of automated radiation monitoring systems and high-tech software and hardware systems for assessment and forecast of radiation emergencies;
- Integrated information space providing the interaction of all participants of emergency response system.
IBRAE RAN develops the following research areas of emergency response:
- Fundamental and applied research on radionuclide dispersal in various environments, including air and water;
- Development and optimization of automated radiation monitoring systems (ARMS), creation of software and hardware for ARMS;
- Development of mobile systems of radiation monitoring and radiation survey;
- Implementation of territorial and facility ARMS created on the basis of models, codes and geoinformation systems developed by IBRAE RAN;
- participation in arrangement of regular emergency exercises carried out in the framework of the federal target programs and international projects;
- Scientific, technical and expert support through the Technical Crisis Centre of IBRAE RAN to response activities in radiation emergencies at the federal, regional and industrial levels.
RADIATION MONITORING SYSTEMS
From the point of view of minimizing the consequences of radiation accidents at NPP and other NRHF, quickness of decision making and implementation of measures to protect the population and environment is of the utmost importance. This necessitates the establishment of effective radiation monitoring systems in the near and far zones of NRHF using up-to-date software and hardware systems and information technologies.
IBRAE RAN in cooperation with RPC "Doza" and JSC "SPC Aspect " is working on creation of automated radiation monitoring systems (ARMS) and development of unified technical specifications for such systems to bring them into line with Russian and international standards. ARMS basis are the stationary meters of ambient equivalent dose rate (AEDR). The need for unification of metrological characteristics of the meters is caused by specific operation of ARMS (field work, requirement of reliable measurement of near-background AEDR values).
Stationary radiation monitoring systems can be divided into two main classes: facility’s ARMS for radiation monitoring at NRHF site and in close proximity and territorial ARMS whose scope covers the entire regions with a large number of NRHF. At present, advanced hybrid monitoring system using mobile radiological laboratories and mobile measurement systems are intensively developing. Such systems provide greater efficiency of management and decision-making in comparison with stationary ARMS.

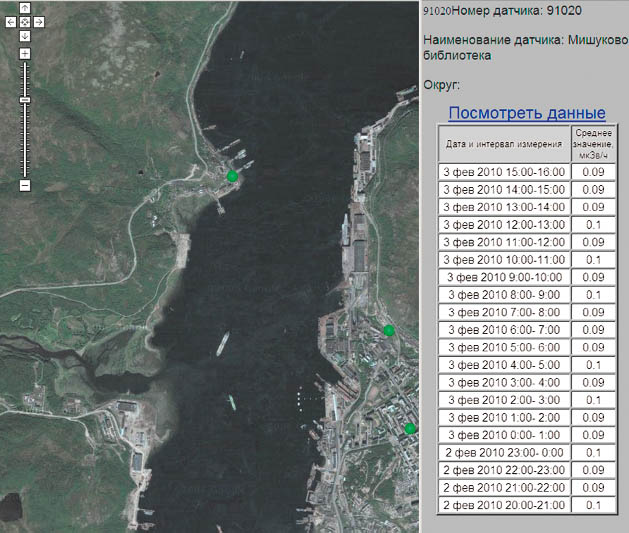
FACILITY ARMS DEVELOPED BY IBRAE RAN
IBRAE RAN develops the facility automated radiation monitoring systems since 1999. The first of these systems, created in the framework of international program AMEC (Arctic Military Environmental Cooperation), was commissioned in April 2004. It was established at FSUE "Atomflot" in Murmansk and designed for ensuring radiation safety of temporary storage of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) of nuclear submarines of the Russian Navy. The system includes 8 stations for monitoring of gamma radiation dose rate, 2 stations to monitor air contamination in the site, 3 stations to monitor alpha- and beta-active aerosols in the ventilation systems, installation for monitoring of radioactive contamination of treated waste water and automatic weather station. Software for collection and transfer of radiation monitoring data was developed at IBRAE RAN; software for visualization of monitoring results was developed in the Norwegian Institute for Energy Technologies and adapted by the experts of IBRAE RAN.
In 2008-2011, within the framework of the federal target program IBRAE experts in cooperation with JSC VNIPIET, RPC "Doza" and JSC "Technocenter service" upgraded ARMS of FSUE "Atomflot". The number of radiation monitoring stations at the site, in the controlled area and the surveillance zone was increased, and they were integrated into automated system with single shared server and software.
Most of facilities ARMS, designed at IBRAE RAN under the federal and international target programs, are located in Murmansk Region ("Nerpa", reactor compartment storages in Zaozersk, Gremikha, Sayda Bay and Andreeva Bay) and Archangelsk Region (JSC PO " Sevmash", JSC “SC Zvezdochka”), where large-scale work on decommissioning of nuclear fleet facilities and remediation of contaminated land and water areas are carried out.
In addition, facilities ARMS were created together with the organizations of the State Corporation "Rosatom", namely the RussianFederalNuclearCenter “All-Russian Research Institute of Experimental Physics” (VNIIEF) and SRC "Research Institute of Atomic Reactors" (NIIAR) on the sites of these institutes.
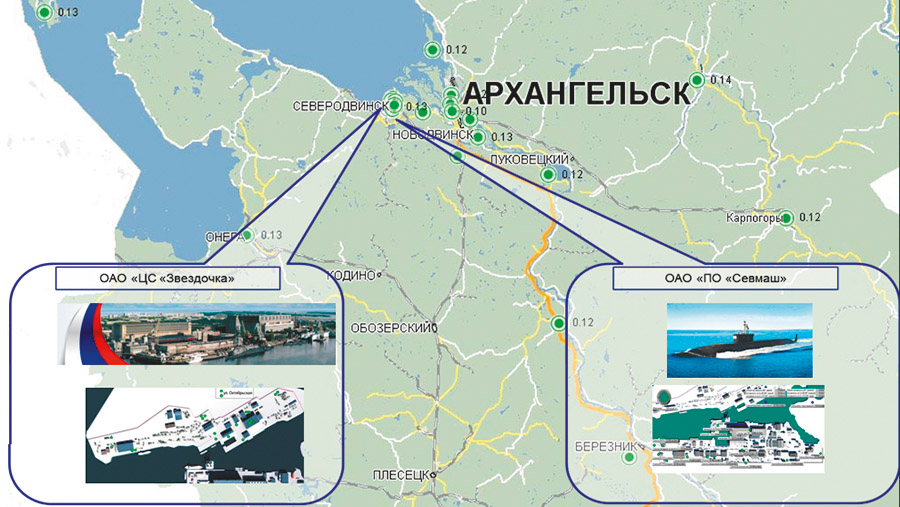
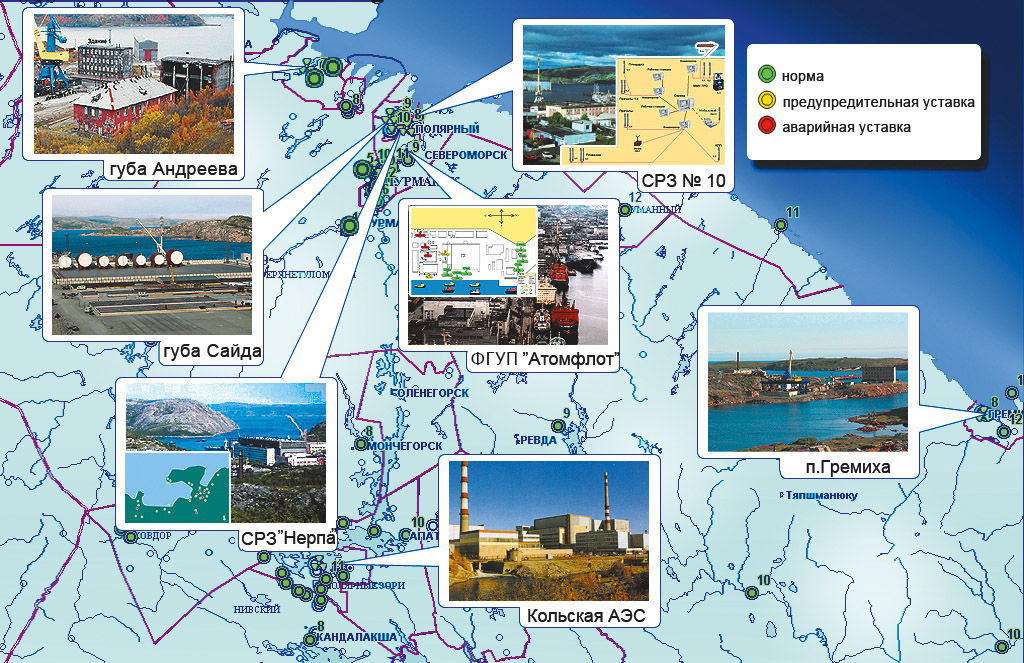
TERRITORIAL ARMS
Territorial ARMS (TARMS) are the foundation of radiation monitoring and emergency response system, providing information support to the actions of federal and regional executive authorities of the Russian Federation for ensuring radiation safety of the population and environment. They are designed with the ability to integrate into a unified automated radiation monitoring system in the territory of the Russian Federation. They are designed for continuous automatic radiation monitoring in the RF region, acquisition, processing and visualization of real-time data about radiation conditions, information exchange with other subsystems, federal, regional and departmental crisis centers.
TARMS STRUCTURE
Typical structure of territorial automated radiation monitoring system consists of data acquisition and processing center (DAPC) and stationary stations of radiation and meteorological monitoring placed in the settlements or on terrain. Data transfer from the monitoring stations to DAPC by telephone lines, the Internet, wireless cellular and radio channels.
The hardware of the radiation monitoring station includes a unit for detecting gamma radiation dose rate and unit for data processing and transfer (DPU), which provides connection to the server DAPC and workstations designed to display the results of monitoring. External electronic bulletin board and an automatic weather station (determines the direction and speed of wind, measures barometric pressure, temperature and relative humidity) can be also connected to DPU.
Commercially available devices, included in the State Register of measuring tools, are used in the ARMS systems developed by IBRAE as the units for detection of ambient equivalent dose of gamma radiation (BDMG-200, DBG-S11Dmn – the gamma radiation dosimeters, IRT-M – the meters of background radiation manufactured by RPC "Doza", Zelenograd, and dosimeters UDRG-50 (STC "Rion"). They allow measuring AEDR in the range of 0.1-107 μSv/h with a relative error less than ± 25%. Certified automatic meteosystem MK-15 (SPA "Typhoon") or weather station «Vaisala Oyj WXT520» (Finland), the advantage of which is the lack of moving parts, are used for collection of meteorological data.
TARMS SOFTWARE
IBRAE software is designed to collect and process data coming from local TARMS stations, to inspect condition and automatic reactivation of detection units, to maintain the databases, to display the radiation conditions using modern GIS technologies, to exchange data with other radiation monitoring systems.
The program "Radiation Condition Monitor" which is installed on the workstation of TARMS operator is used for real-time visualization of the results of radiation monitoring. Multi-windows Windows-interface of the program includes a control panel, the windows of geographical map and the current values of sensors. The program allows displaying the data about radiation conditions in geo-referenced graphical and tabular forms, generating the reports and operational trends, monitoring the current status of individual elements and whole ARMS system.
Tablet computers for remote monitoring
IBRAE RAN has developed web-application "Web- monitoring Server" based on geoinformation technologies. The application is designed for installation on mobile devices (tablets and smartphones) and allows staff of ARMS control centers to monitor the radiation conditions remotely.
TERRITORIAL ARMS DEVELOPED IN COOPERATION WITH IBRAE RAN
In 2005-2008, TARMS was established in the Murmansk Region. The system was developed by IBRAE RAN within the project “Enhancement of Radiation Monitoring and Emergency Response System in the Murmansk Region". Then the number of stations for gamma dose rate monitoring and weather stations were increased during the subsequent upgrade of TARMS. Data interchange with departmental radiation monitoring systems located in the region (in particular, with the ARMS of Kola NPP) was organized. The Data Acquisition and ProcessingCenter was established in the Murmansk Centre for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring. The Center has the data transfer channels to the Crisis Center of EMERCOM Department in the Murmansk Region and to the Situation Centre of the Government of the Murmansk Region.
In 2008-2010, IBRAE RAN participated in the international project "Enhancement of the System of Radiation Monitoring and Emergency Response in the Archangelsk Region". Territorial Radiation Monitoring and Emergency Response System was established, which includes 25 AEDR monitoring stations, two automatic weather stations and DAPC in the ArkhangelskCenter of hydrometeorology and environmental monitoring. Data about the radiation conditions also come to the Crisis Center of EMERCOM and the Situation Centre of the Government of the Arkhangelsk Region.
In total, from 2005 to 2013, 22 regional automated radiation monitoring and emergency response systems were established in various regions of the Russian Federation by IBRAE (or with the active participation of its experts) in cooperation with Rosatom, EMERCOM and Roshydromet under various federal and international projects. In addition, software for TARMS monitoring stations and control centers was developed in cooperation with SPA "Taifun" of Roshydromet.
The systems of Murmansk and Arkhangelsk Regions have been recommended by IAEA mission as the models of such systems for other regions of Russia. Summing up the results of the international project "Enhancement of the System of Radiation Monitoring and Emergency Response in the Archangelsk Region" in July 2011, IAEA experts emphasized that the project "... is unique both in the number of participants and coverage areas. The organization of work under the project and the results are worthy of high appraisal. "
The projects on enhancement of territorial radiation monitoring and emergency response systems in the Murmansk (2005-2008.) and Archangelsk (2008-2012) Regions are the examples (see pdf-presentations in Russian and English languages).
PROMISING ARMS TOOLS
Development of new industries leads to a steady increase in the number of NRHF and growth of the hazards, so the most effective radiation monitoring technologies should be used for creating ARMS systems. IBRAE RAN studies of advanced monitoring concepts are of great scientific and practical importance and can be the basis for implementation of new generation of ARMS systems.
HYBRID RADIATION MONITORING
The concept of so-called hybrid monitoring treats ARMS as a unified measuring and calculating system that provides a continuous process of adapting the radionuclide dispersal model to the specific conditions based on the results of field measurements. Monitoring structure designed for achieving the following objectives: timely, already in early phase of accident, detection of atmospheric release (or liquid discharge) of radionuclides; express assessment of source activity or dose rate; monitoring of radiation conditions in the area of real radioactive contamination. Unlike the typical monitoring schemes, the main tools of measurement are the mobile radiometric laboratories (MRL). Monitoring stations are used to determine the shape of radiation trace.
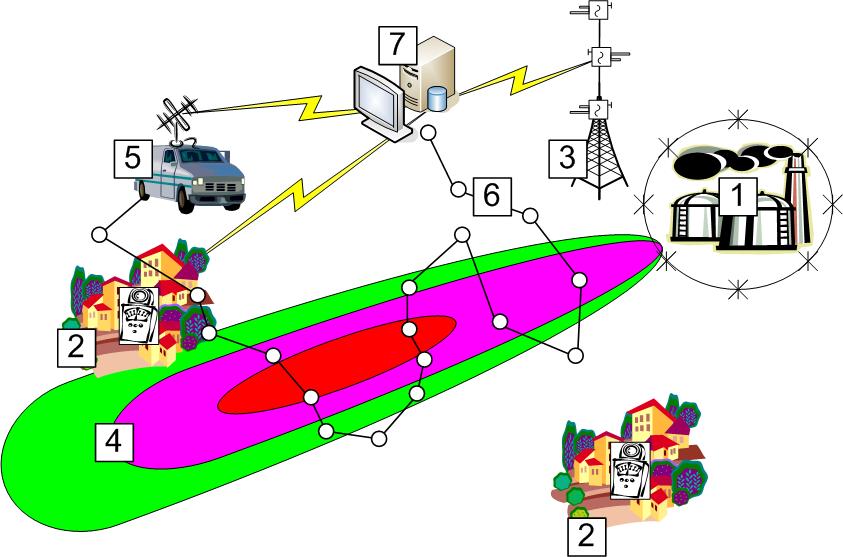
The structure of hybrid monitoring
1 — NRHF, 2 — dosimetric stations,
3 — stationary meteorological mast near NRHF, 4 — contaminated area (trace) after radioactive release,
5 — MRL, 6 — MRL route and measurement points, 7 — ARMS DAPC
MOBILE RADIOMETRIC LABORATORIES
Mobile radiometric laboratories operate as part of facilities’-and territorial ARMS. They used for refinement of data from fixed radiation monitoring stations, as well as for radiation survey outside the monitoring stations. MRL use significantly increases ARMS effectiveness and efficiency of decision-making of emergency response participants.
IBBRAE RAN, RPC "Doza", LLC "Avtospektr-NN" and LLC "Autolic" jointly developed and put into operation more than twenty mobile radiometric laboratories on the chassis of vans or off-road vehicles. They are designed for independent work in the field and perform the following main tasks:
- Detection and localization of radioactive sources of contamination;
- Mapping of the boundaries of contaminated areas;
- Identification of contamination parameters;
- Sampling of soil, water and air;
- Real-time transfer of measurement data to crisis centers.


MRL consists of measuring and dosimetric equipment, computer system (industrial protected computer «Advantech» PPC-154T or equivalent) with integrated application software, videounits, navigation tools, satellite and mobile communications devices, devices for sampling of soil, water and air and express analysis of the samples. The main measuring tool is spectrally sensitive dosimetric installation "Gamma-sensor", which allows gamma survey, determination of nuclide composition of contamination source, accurate geo-referenced measurements with data plotting on electronic map, database maintaining and real-time transfer of measurement data to the crisis centers.
A specialized program "Sensor" is developed at RPC "Doza" to work with the "Gamma-sensor" installation. It provides control of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and GPS satellite navigation system, calculation of equivalent dose rate at the point of detector placement and assessment of radionuclides contribution to the dose, display of measured energy and dose gamma spectra with the possibility of scaling.
 |
IBRAE RAN © 2013-2024 | Site map | Feedback |